Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DMKINJO)
| Drug Name |
Gentamicin
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Alcomicin; Apogen; Bristagen; Cidomycin; GENTAMYCIN; Garamycin; Garasol; Gentacidin; Gentacycol; Gentafair; Gentak; Gentamar; Gentamicina; Gentamicine; Gentamicins; Gentamicinum; Gentamycinum; Gentavet; Gentocin; Jenamicin; Refobacin; Uromycine; Garamycin Otic Solution; Genoptic Liquifilm; Gentamcin Sulfate; Gentamicin sulphate sterile; Refobacin TM; Gentamicin C1; G-Mycin; G-Myticin; Garamycin (TN); Gentamicin (BAN); Gentamicin (TN); Gentamicina [INN-Spanish]; Gentamicine [INN-French]; Gentamicinum [INN-Latin];Gentamycin-creme; Gentamycin-creme [German]; Ocu-Mycin; Spectro-Genta; U-Gencin; Genoptic S.O.P.; O-2-amino-2,3,4,6,7-pentadeoxy-6-(methylamino)-alpha-D-ribo-heptopyranosyl-(1-4)-O-(3-deoxy-4-C-methyl-3-(methylamino)-beta-L-arabinopyranosyl-(1-6))-2-deoxy-D-streptamine; (1R,2S,3S,4R,6S)-4,6-diamino-3-[3-deoxy-4-C-methyl-3-(methylamino)-beta-L-arabinopyranosyloxy]-2-hydroxycyclohexyl 2-amino-2,3,4,6,7-pentadeoxy-6-(methylamino)-beta-L-lyxo-heptopyranoside; (1R,2S,3S,4R,6S)-4,6-diamino-3-{[3-deoxy-4-C-methyl-3-(methylamino)-beta-L-arabinopyranosyl]oxy}-2-hydroxycyclohexyl (6x)-2-amino-2,3,4,6,7-pentadeoxy-6-(methylamino)-alpha-D-erythro-heptopyranoside; (2R,3R,4R,5R)-2-[(1S,2S,3R,4S,6R)-4,6-diamino-3-[(2R,3R,6S)-3-amino-6-[1-(methylamino)ethyl]oxan-2-yl]oxy-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)oxane-3,5-diol; 2-[4,6-diamino-3-[3-amino-6-[1-(methylamino)ethyl]oxan-2-yl]oxy-2-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy-5-methyl-4-(methylamino)oxane-3,5-diol; 4,6-diamino-3-{[3-deoxy-4-c-methyl-3-(methylamino)pentopyranosyl]oxy}-2-hydroxycyclohexyl 2-amino-2,3,4,6,7-pentadeoxy-6-(methylamino)heptopyranoside
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antibiotics
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Enteric bacteria and other eubacteriaPseudomonas aeruginosaYersinia pestisFrancisella tularensisProteus vulgarisSerratia marcescens
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
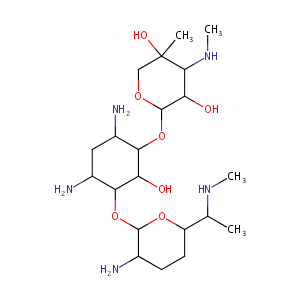 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 3 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 477.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | -4.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Adverse Drug Reaction (ADR) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Combinatorial Drugs (CBD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed CBD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Same Disease as Gentamicin
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Gentamicin (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug Inactive Ingredient(s) (DIG) and Formulation(s) of This Drug
References
| 1 | Gentamicin FDA Label | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 2427). | ||||
| 3 | Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds | ||||
| 4 | DailyMed Drug Label Information: Gentamicin sulfate injection | ||||
| 5 | Pharmacokinetics of gentamicin in children and adults. J Infect Dis. 1975 Dec;132(6):637-51. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.6.637. | ||||
| 6 | Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose | ||||
| 7 | ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899. | ||||
| 8 | Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. U.S. Department of Health & Human Services. | ||||
| 9 | Cloning and expression of novel aminoglycoside phosphotransferase genes from Campylobacter and their role in the resistance to six aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Dec 21;62(1). pii: e01682-17. | ||||
| 10 | Relationship between antimicrobial resistance and aminoglycoside-modifying enzyme gene expressions in Acinetobacter baumannii. Chin Med J (Engl). 2005 Jan 20;118(2):141-5. | ||||
| 11 | Detection of multidrug-resistant Enterobacteriaceae isolated from river waters flowing to the Guanabara Bay and from clinical samples of hospitals in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Biomedica. 2019 May 1;39(s1):135-149. | ||||
| 12 | Expression of Clostridium thermocellum endoglucanase gene in Lactobacillus gasseri and Lactobacillus johnsonii and characterization of the genetically modified probiotic lactobacilli. Curr Microbiol. 2000 Apr;40(4):257-63. | ||||
| 13 | Alpha-L-iduronidase premature stop codons and potential read-through in mucopolysaccharidosis type I patients. J Mol Biol. 2004 Apr 30;338(3):453-62. | ||||
| 14 | Investigations on the potential nephrotoxicity of cefazedone and gentamicin and of their combination, in comparison with the combination of cefazolin and cephalothin with gentamicin. Arzneimittelforschung. 1979;29(2a):449-52. | ||||
| 15 | Classification and rescue of ROMK mutations underlying hyperprostaglandin E syndrome/antenatal Bartter syndrome. Kidney Int. 2003 Sep;64(3):923-32. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00153.x. | ||||
| 16 | In vitro evaluation of biomarkers of nephrotoxicity through gene expression using gentamicin. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2018 Sep;32(9):e22189. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22189. Epub 2018 Jul 10. | ||||
| 17 | The absence of nephrotoxicity and differential nephrotoxicity between tobramycin and gentamicin. South Med J. 1990 Oct;83(10):1149-52. doi: 10.1097/00007611-199010000-00008. | ||||
| 18 | Agencia Espaola de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios Healthcare "Centro de informacion online de medicamentos de la AEMPS - CIMA.". | ||||
| 19 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.". | ||||
| 20 | FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration "FDA Drug Safety Communication: Low magnesium levels can be associated with long-term use of proton pump inhibitor drugs (PPIs).". | ||||
| 21 | Engle JE, Drago J, Carlin B, Schoolwerth AC "Letter: Reversible acute renal failure after cephalothin." Ann Intern Med 83 (1975): 232-3. [PMID: 1147461] | ||||
| 22 | Cerner Multum, Inc. "UK Summary of Product Characteristics.". | ||||
| 23 | Chang JT, Green L, Beitz J "Renal failure with the use of zoledronic acid." N Engl J Med 349 (2003): 1676-9 discussion 1676-9. [PMID: 14573746] | ||||
| 24 | Wong GT, Lee EY, Irwin MG. Contrast induced nephropathy in vascular surgery.?Br J Anaesth. 2016;117 Suppl 2:ii63-ii73. [PMID: 27566809] | ||||
| 25 | Assael BM, Chiabrando C, Gagliardi L, Noseda A, Bamonte F, Salmona M "Prostaglandins and aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity." Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 78 (1985): 386-94. [PMID: 4049389] | ||||
| 26 | Burkett L, Bikhazi GB, Thomas KC Jr, Rosenthal DA, Wirta MG, Foldes FF "Mutual potentiation of the neuromuscular effects of antibiotics and relaxants." Anesth Analg 58 (1979): 107-15. [PMID: 571233] | ||||
| 27 | Product Information. CellCept (mycophenolate mofetil). Roche Laboratories, Nutley, NJ. | ||||
| 28 | Bates DE, Beaumont SJ, Baylis BW "Ototoxicity induced by gentamicin and furosemide." Ann Pharmacother 36 (2002): 446-51. [PMID: 11895059] | ||||
| 29 | Athlin L, Domellof L, Holm S "Gentamicin treatment in severe surgical infections: serum levels, interactions, toxicity and efficacy." Acta Chir Scand 147 (1981): 225-30. [PMID: 7034430] | ||||
| 30 | Farag MM, Mikhail MR, Abdel-Meguid E, Abdel-Tawab S "Assessment of gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats treated with low doses of ibuprofen and diclofenac sodium." Clin Sci 91 (1996): 187-91. [PMID: 8795442] | ||||
| 31 | Product Information. Exjade (deferasirox). Novartis Pharmaceuticals, East Hanover, NJ. | ||||
| 32 | Product Information. Paraplatin (carboplatin). Bristol-Myers Squibb, Princeton, NJ. | ||||
| 33 | Product Information. Prograf (tacrolimus). Fujisawa, Deerfield, IL. | ||||
| 34 | Novis BH, Korzets Z, Chen P, Bernheim J "Nephrotic syndrome after treatment with 5-aminosalicylic acid." Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 296 (1988): 1442. [PMID: 3132281] | ||||
